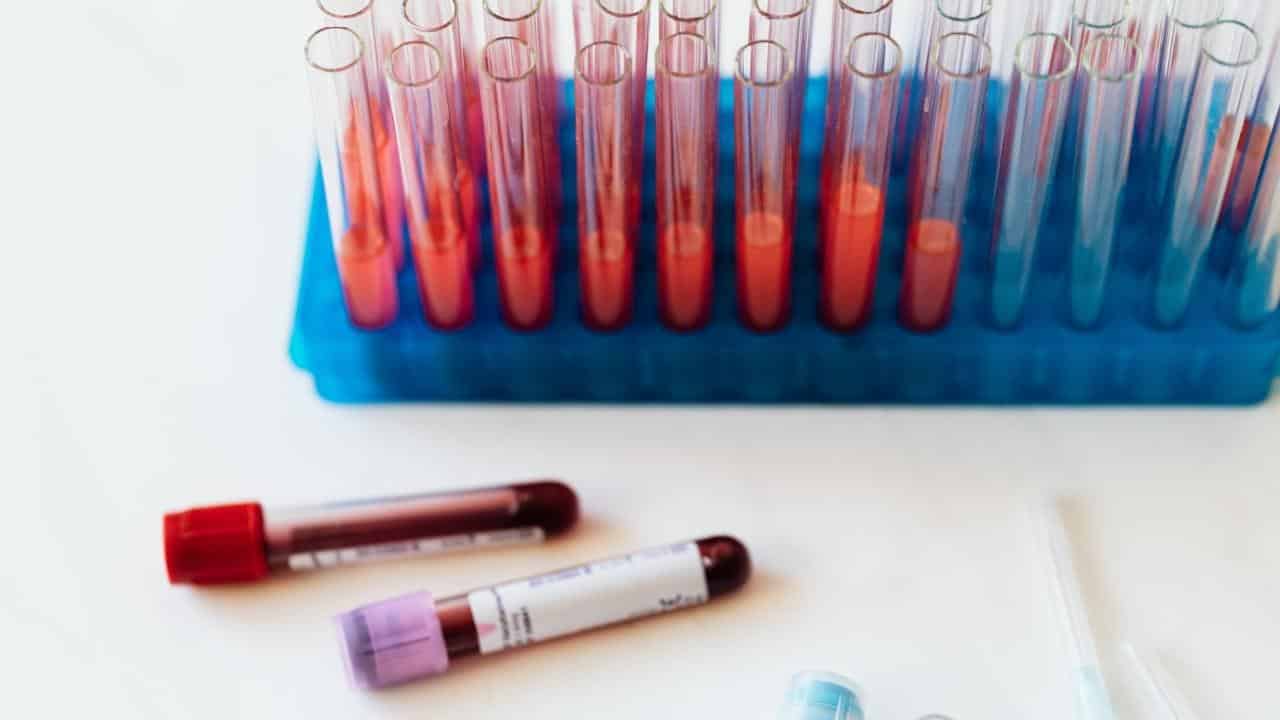
Coagulation Test
what is Coagulation Test and why should you do it?
Coagulation testing refers to laboratory blood tests that provide vital information about the body's ability to form and dissolve blood clots. Key examples include prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), fibrinogen levels, and platelet counts. These tests help identify bleeding disorders like hemophilia, as well as clotting disorders like deep vein thrombosis.
PT and aPTT tests measure the time it takes for blood to clot and evaluate the functioning of the coagulation cascade. Prolonged clotting times indicate a greater risk of uncontrolled bleeding. Meanwhile, low fibrinogen levels or platelet counts also raise the risk of bleeding problems.
On the other hand, shortened clotting times may signal increased clotting tendency and risk of dangerous clots forming in the veins or arteries. Elevated fibrinogen or high platelet counts can also increase clotting risk.
More on the importance of coagulation testing
Coagulation test helps diagnose the cause of symptoms like easy bruising, nosebleeds, heavy menstruation, blood in the urine or stool. It also guides treatment approaches. For example, patients with bleeding disorders may be treated with transfusions of platelets or fresh frozen plasma. Anticoagulant therapy helps manage those prone to clotting.
Before surgeries and procedures, coagulation tests assess if bleeding risks are elevated. Results inform the need for transfusions or changing medications pre-operatively to minimize complications. Ongoing testing also monitors the effects of anti-clotting drugs like warfarin.
In summary about Coagulation Test
Coagulation blood tests provide crucial guidance for detecting and caring for patients with hematological disorders affecting clotting and bleeding. They help improve patient safety and outcomes.
ייעוץ חינם 24/7
לכל שאלה השארו פרטים :